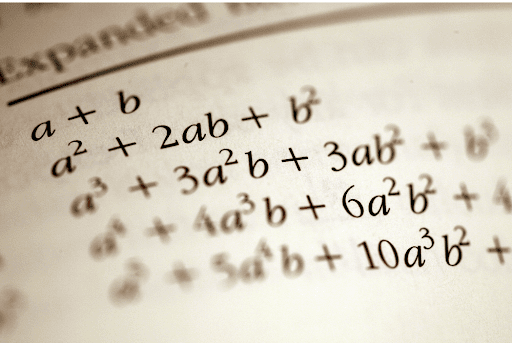📘 About Algebra
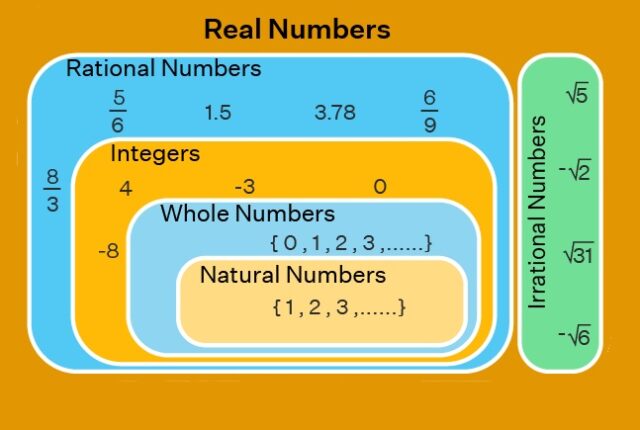
Algebra is the branch of mathematics that uses symbols, usually letters, to represent numbers in formulas and equations. It helps us describe patterns, solve problems, and think logically.
At its core, Algebra is about finding the unknown and understanding how variables relate to each other.
🔤 Key Concepts in Algebra
-
Variables: Letters like xx, yy, or nn used to stand for unknown values.
-
Expressions: Mathematical phrases, e.g. 3x+23x + 2, that do not have an equals sign.
-
Equations: Expressions that are set equal to each other, e.g. 2x+3=112x + 3 = 11
-
Solving: Finding the value of the variable that makes the equation true.
-
Substitution: Replacing a variable with a known value.
-
Factorising: Writing expressions in a simpler or more useful form, e.g. x2+5x+6=(x+2)(x+3)x^2 + 5x + 6 = (x+2)(x+3)
-
Expanding brackets: Multiplying out expressions, e.g. (x+2)(x+3)=x2+5x+6(x + 2)(x + 3) = x^2 + 5x + 6
📊 Skills Developed
-
Logical reasoning and abstract thinking.
-
Applying formulas to solve real-life problems.
-
Foundation for advanced mathematics like calculus and data analysis.
🧠 Example Topics
-
Solving linear equations:
2x+5=15⇒x=52x + 5 = 15 \Rightarrow x = 5 -
Simplifying expressions:
3x+4x=7x3x + 4x = 7x -
Using formulas:
A=l×wA = l \times w (area of a rectangle) -
Forming equations:
If each apple costs $x, then 4 apples cost 4x4x -
Working with inequalities:
2x−1>7⇒x>42x - 1 > 7 \Rightarrow x > 4
- Afternoon Class, Evening Class
- Mathematics
- 1
- 1 hours
- Members
- : 50